Open Research Internship position in
Cooperative multi-robot non-prehensile manipulation
Short abstract: The goal of this Master Thesis is to propose novel distributed control algorithms for the non-prehensile manipulation of unknown objects with a group of mobile robots.
Team: Rainbow IRISA/Inria Rennes, France
Advised by: Esteban Restrepo and Paolo Robuffo Giordano
Contact: esteban.restrepo@irisa.fr – prg@irisa.fr
How to apply: Interested candidates are requested to apply via this form.
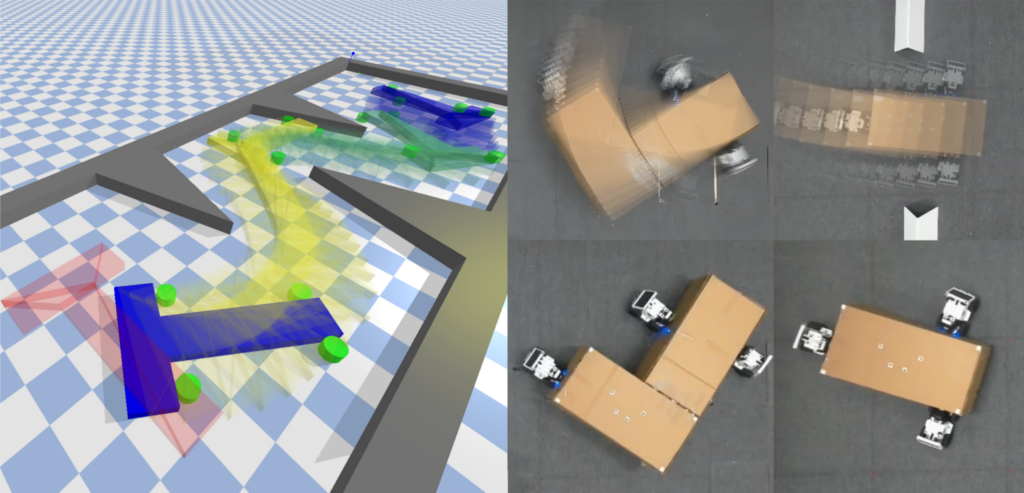
Description: How can a team of robots work together to transport unknown objects without prior knowledge of their properties? This Master’s thesis aims to develop innovative distributed control algorithms that enable a group of mobile robots to autonomously manipulate objects of unknown properties (mass, friction, and center of mass), overcoming sensing and actuation constraints through intelligent collaboration.
Motivations: Pushing is one of the simplest yet most powerful ways for robots to interact with their environment, with applications spanning from warehouse logistics to autonomous construction and precision agriculture. While traditional approaches rely on a single robot—often a robotic arm in controlled settings—real-world scenarios demand more flexibility.
Multi-robot teams offer a promising alternative, allowing for scalable and robust non-prehensile manipulation strategies. However, current methods often assume prior knowledge of object properties or impose restrictive configurations, limiting their applicability to dynamic and unpredictable environments. This project seeks to bridge that gap by designing adaptive and distributed control strategies for teams of mobile robots engaged in collaborative pushing.
General Objectives: The goal of this Master Thesis is to develop novel distributed control algorithms, based on pinning consensus [1], that allow a team of mobile robots to push and manipulate objects without prior knowledge of their properties. Moreover, the team of robots should be able to adapt and reconfigure dynamically when dealing with different objects, taking into account constraints such as limited sensing range, field of view, and actuation capabilities. Moreover, the student will help to setup and develop a multi-robot testbed based on the Cambridge RoboMaster platform [2] to validate the proposed algorithms both in simulation and in real-world experiments.
This thesis will provide exciting opportunities to explore cutting-edge control methodologies for multi-robot collaboration.
Envisaged Activities
-
Literature review of the related works and familiarize with the experimental setup in the team
-
Take over the existing works and work on the design and analysis of a control algorithm for autonomous pushing of unknown objects with multi-robot systems
-
Implement a simulatior for validating the proposed algorithms
-
Help setup the hardware and software for a team of holonomic ground robots able to perform the manipulation task
-
Validate experimentally the scenario on the team of mobile robots
Skills/Requirements
- High motivation and interest in the topic
- Good experience with robotics hardware and software (Python/C++ and ROS2)
- Knowledge in control theory and robot modeling
- Basic knowledge of control and analysis of multi-agent systems is appreciated
- Scientific curiosity
Conditions
Expected duration of the internship: 5-7 months
The work will be carried in English at the Centre Inria de l’Université de Rennes research center in Rennes, France.
Financial support offered to the student: gratification de 4,35 € / h
How to apply
Interested candidates are requested to apply via this form.
The position will remain open until a satisfactory candidate is found. In case of positive feedback, you will be contacted. If not positive, you won’t hear back.
Supervisor(s): Dr. Esteban Restrepo and Dr. Paolo Robuffo Giordano
References
-
Song, Q., Cao, J., & Yu, W. (2010). Second-order leader-following consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems via pinning control. Systems & Control Letters, 59(9), 553-562.
-
Blumenkamp, J., Shankar, A., Bettini, M., Bird, J., & Prorok, A. (2024). The cambridge robomaster: An agile multi-robot research platform. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.02198.
-
Rosenfelder, M., Ebel, H., & Eberhard, P. (2022, August). A force-based control approach for the non-prehensile cooperative transportation of objects using omnidirectional mobile robots. In 2022 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA) (pp. 349-356). IEEE.
-
Bertoncelli, F., & Sabattini, L. (2021, December). Planar Pushing Manipulation with a Group of Mobile Robots. In 2021 20th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR) (pp. 897-904). IEEE.
-
Tang, Z., Feng, Y., & Guo, M. (2024). Collaborative Planar Pushing of Polytopic Objects with Multiple Robots in Complex Scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.07908.
-
Robuffo Giordano, P., Franchi, A., Secchi, C., & Bülthoff, H. H. (2013). A passivity-based decentralized strategy for generalized connectivity maintenance. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 32(3), 299-323.
-
Bertoncelli, F., Selvaggio, M., Ruggiero, F., & Sabattini, L. (2022, October). Task-oriented contact optimization for pushing manipulation with mobile robots. In 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (pp. 1639-1646). IEEE.



