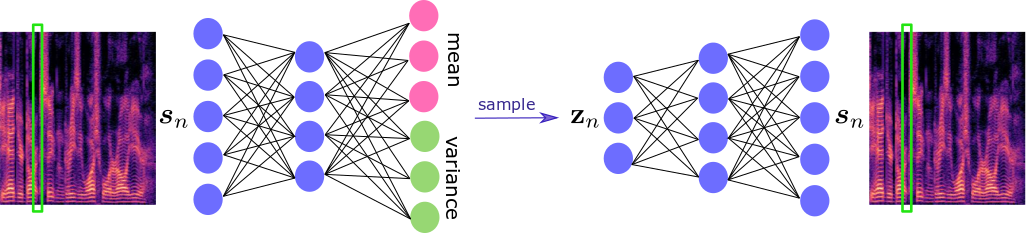
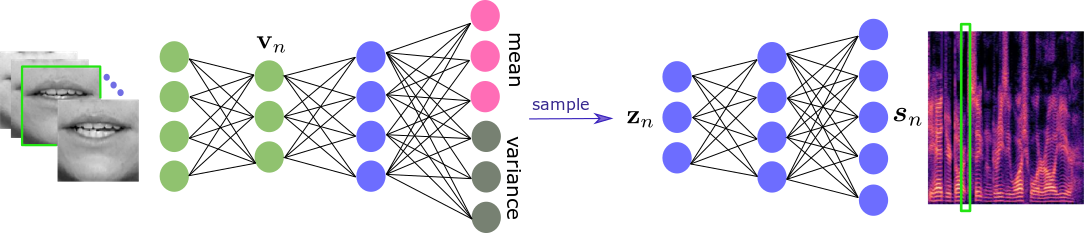
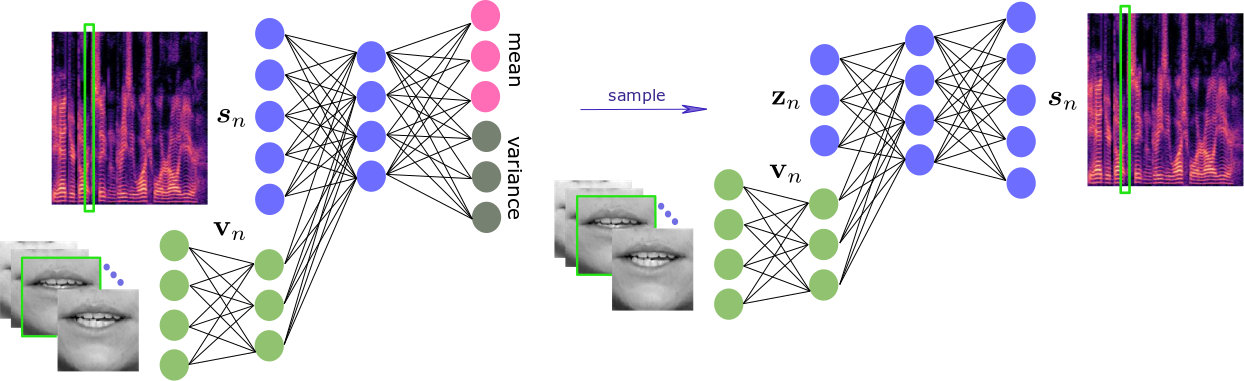
Audio-visual Speech Enhancement Using Conditional Variational Auto-Encoder
Mostafa Sadeghi, Simon Leglaive, Xavier Alameda-Pineda, Laurent Girin, Radu Horaud
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, volume 28, 2020, 1788-1800 | IEEEXplore | arXiv| Python code
Abstract. Variational auto-encoders (VAEs) are deep generative latent variable models that can be used for learning the distribution of complex data. VAEs have been successfully used to learn a probabilistic prior over speech signals, which is then used to perform speech enhancement. One advantage of this generative approach is that it does not require pairs of clean and noisy speech signals at training. In this paper, we propose audio-visual variants of VAEs for single-channel and speaker-independent speech enhancement. We develop a conditional VAE (CVAE) where the audio speech generative process is conditioned on visual information of the lip region. At test time, the audio-visual speech generative model is combined with a noise model based on nonnegative matrix factorization, and speech enhancement relies on a Monte Carlo expectation-maximization algorithm. Experiments are conducted with the recently published NTCD-TIMIT dataset. The results confirm that the proposed audio-visual CVAE effectively fuse audio and visual information, and it improves the speech enhancement performance compared with the audio-only VAE model, especially when the speech signal is highly corrupted by noise. We also show that the proposed unsupervised audio-visual speech enhancement approach outperforms a state-of-the-art supervised deep learning method.
This work was supported by the Multidisciplinary Institute in Artificial Intelligence (MIAI).
Noisy speech signals were selected from the test set provided in the NTCD-TIMIT dataset [1]. Here, we compare two proposed methods, called “V-VAE” and “AV-CVAE”, with the following speech enhancement methods:
- The supervised audio-visual method proposed in [2] (denoted by “Supervised”);
- The unsupervised VAE-based method proposed in [3] (denoted by “A-VAE”).
[1] A. H. Abdelaziz, “NTCD-TIMIT: A new database and baseline for noise-robust audio-visual speech recognition,” in INTERSPEECH, 2017, pp. 3752–3756.
[2] A. Gabbay et al., “Visual speech enhancement,” in Interspeech, 2019.
[3] S. Leglaive et al., “A variance modeling framework based on variational autoencoders for speech enhancement,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop Machine Learning Signal Process. (MLSP),
2018.
| Noise type | Clean | Noisy | Enhanced speech | |||
| “Supervised” | “A-VAE” | “V-VAE” | “AV-CVAE” | |||
| Living room | ||||||
| White | ||||||
| Cafe | ||||||
| Car | ||||||
| Street | < | |||||
| Babble | ||||||
| Noisy | “Supervised” | “A-VAE” |
| Noisy | “V-VAE” | “AV-CVAE” |