SLOWS is a C-platform that can be used to simulate near shore hydrodynamics, wave transformations processes, etc. It allows an accurate simulation of free surface flows on arbitrary topographies with both static and time dependent unstructured mesh adaptation. Both hydrostatic and non hydrostatic flows can be simulated, based on a depth averaged approach.
The kernel of the CODE allows triangle-based residual distribution or finite volume simulations both in Cartesian and spherical (or Mercator) curvilinear coordinates. A mass conserving mesh movement method to adapt an initial grid to wet-dry interfaces as well as to other physical features of the flow, is available. For more robust adaptive mesh deformation one should use the fmg library (more info here). Time marching options involve either high order and (conditionally) positivity preserving implicit schemes, (conditionally) positivity preserving genuinely explicit schemes, as well as high order unconditionally positivity preserving space-time schemes. Newton and frozen Newton loops are used for the implicit nonlinear equations when necessary. An independent library has been developed allowing to enhance the shallow water by inverting an elliptic (grad-div type) PDE providing an algebraic correction providing fully nonlinear and weekly dispersive effects, allowing to recover (frequency enhanced) Green-Naghdi solutions. The elliptic system is discretised using a continuous Galerkin method. Linear algebraic sparse systems are currently solved with MUMPS. Some OpenMp optimization for the shallow water kernel is available.
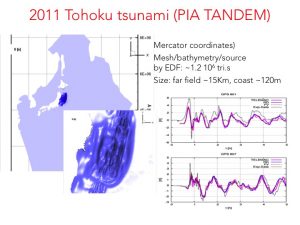
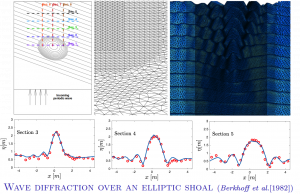
Some examples of computations perfomed with SLOWs are reported in the pictures. For more please have a look at the Gallery on Unstructured grid modelling of coastal hazards and urban floods
THE SOURCES OF SLOWs ARE AVAILABLE HERE.
Please contact Mario Ricchiuto or Maria Kazolea for more information