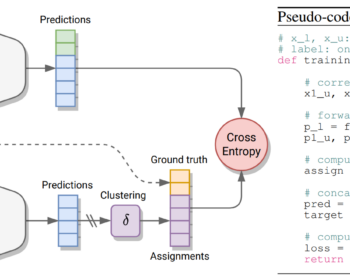
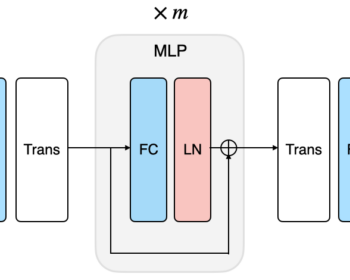
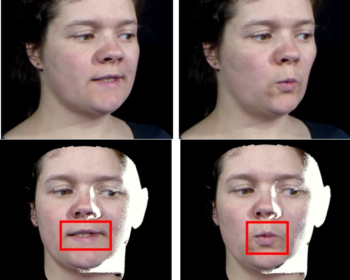
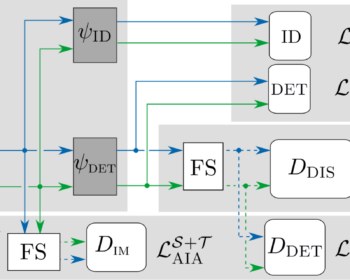
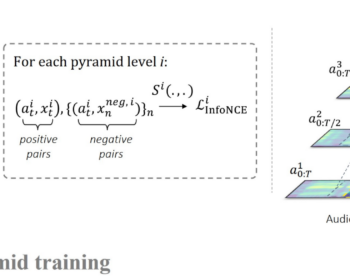Autoregressive GAN for Semantic Unconditional Head Motion Generation
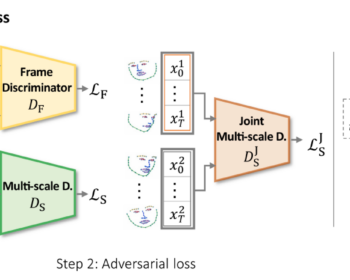
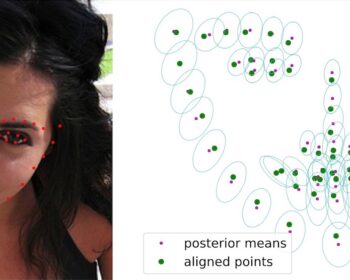
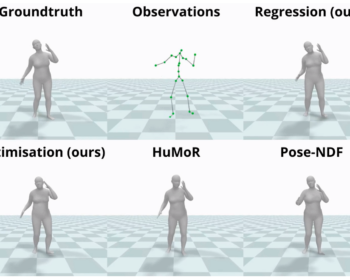
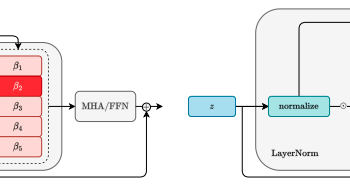
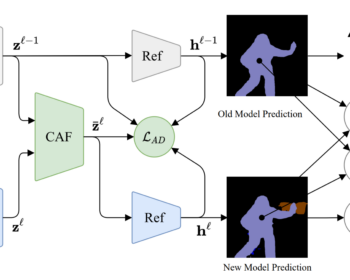
by Louis Airale, Xavier Alameda-Pineda, Stéphane Lathuilière, and Dominique Vaufreydaz ACM Transactions on Multimedia Tools and Applications [paper][code] Abstract: We address the task of unconditional head motion generation to animate still human faces in a low-dimensional semantic space. Deviating from talking head generation conditioned on audio that seldom emphasizes realistic…