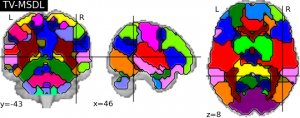
Spontaneous brain activity reveals mechanisms of brain function and dysfunction. Its population-level statistical analysis based on functional images often relies on the de nition of brain regions that must summarize e ciently the covariance structure between the multiple brain networks. In this paper, we extend a network-discovery approach, namely dictionary learning, to readily extract brain regions. To do so, we intro duce a new tool drawing from clustering and linear decomposition methods by carefully crafting a penalty. Our approach automatically extracts regions from rest fMRI that better explain the data and are more stable across subjects than reference decomposition or clustering methods (see FIg. 6 ).
More details can be found here
Figure 6. Regions extracted with the different strategies (colors are random). Please note that a 6mm smoothing has been applied to data before ICA to enhance region extraction.