by Zhiqi Kang, Mostafa Sadeghi, Radu Horaud and Xavier Alameda-Pineda
International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023, 131 (5), pp.1122-1140 

Abstract. Face frontalization consists of synthesizing a frontally-viewed face from an arbitrarily-viewed one. The main contribution of this paper is a frontalization methodology that preserves non-rigid facial deformations in order to boost the performance of visually assisted speech communication. The method alternates between the estimation of (i) the rigid transformation (scale, rotation, and translation) and (ii) the non-rigid deformation between an arbitrarily-viewed face and a face model. The method has two important merits: it can deal with non-Gaussian errors in the data and it incorporates a dynamical face deformation model. For that purpose, we use the generalized Student t-distribution in combination with a linear dynamic system in order to account for both rigid head motions and time-varying facial deformations caused by speech production. We propose to use the zero-mean normalized cross-correlation (ZNCC) score to evaluate the ability of the method to preserve facial expressions. The method is thoroughly evaluated and compared with several state-of-the-art methods, either based on traditional geometric models or on deep learning. Moreover, we show that the method, when incorporated into deep learning pipelines, namely lip reading and speech enhancement, improves word recognition and speech intelligibility scores by a considerable margin.
Examples. Frontalization with OuluVS2 Dataset.
Frontalized face images:
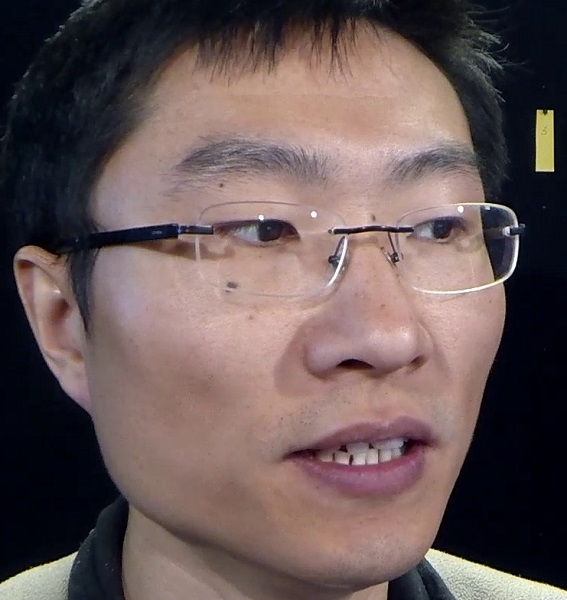
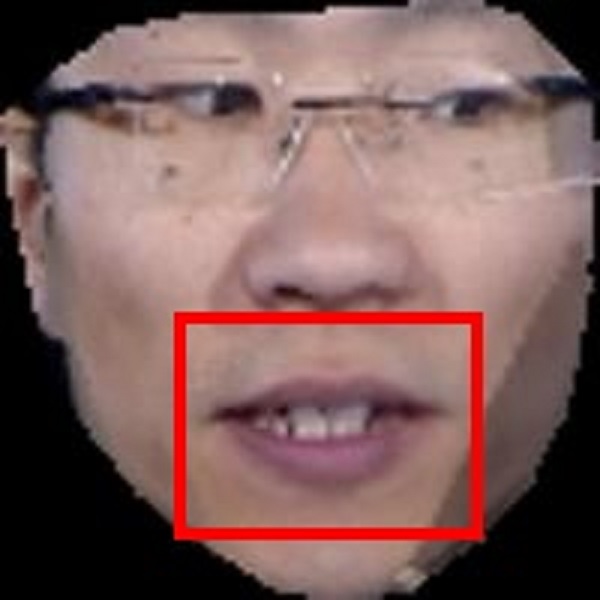

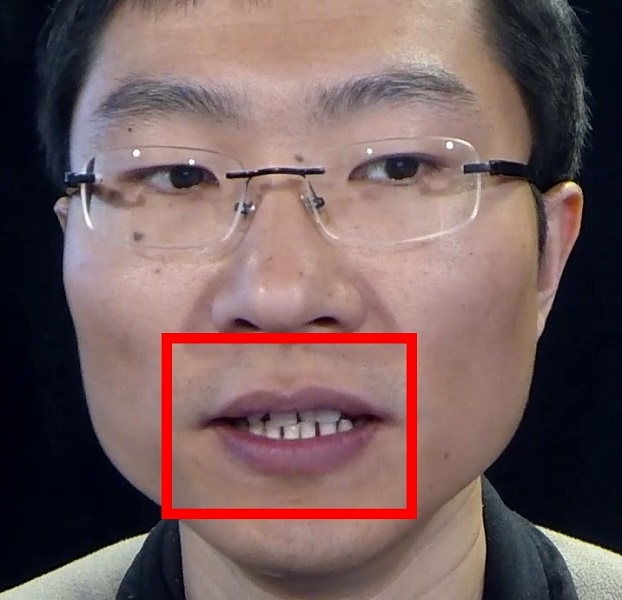
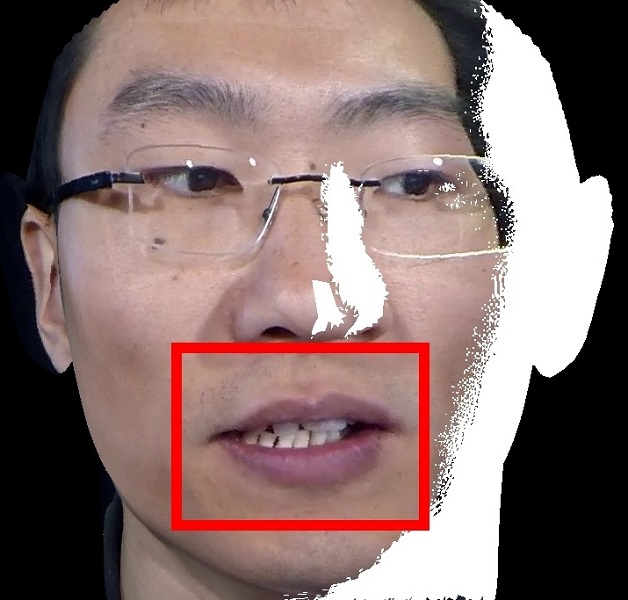

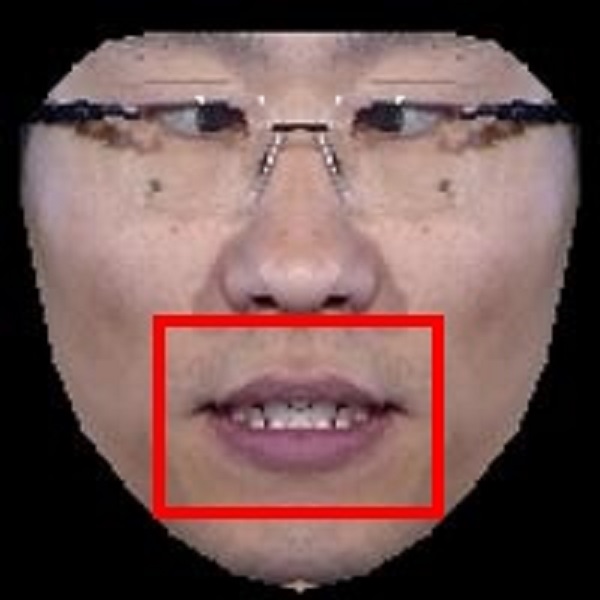
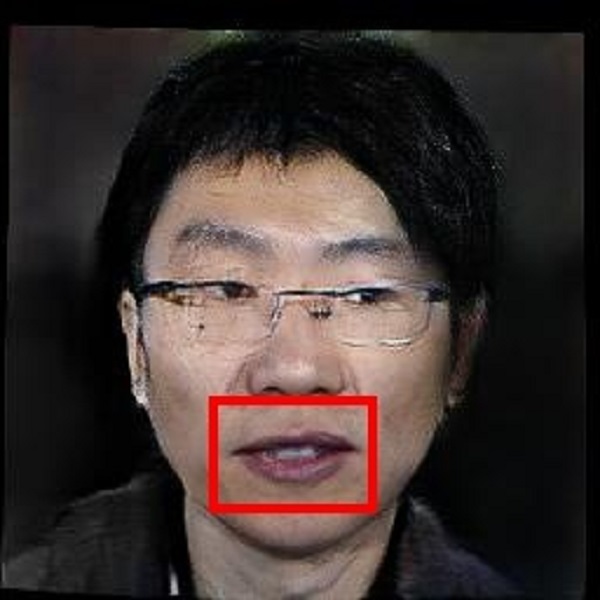
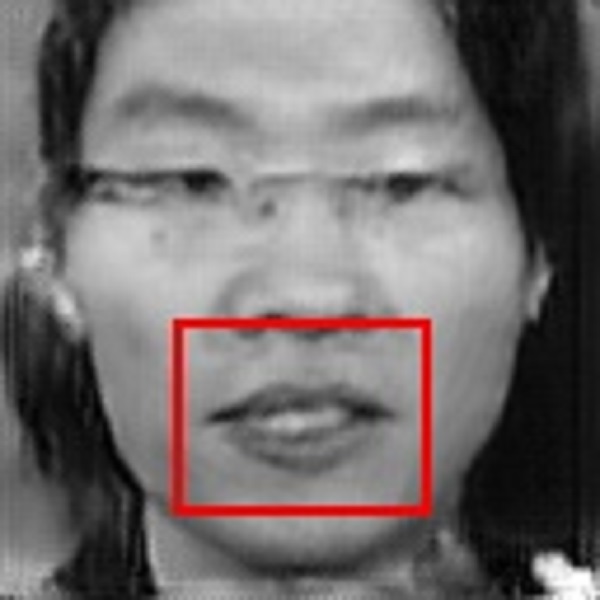
Frontalized lip region videos:
Input Ground truth Proposed Hassner et al. Banerjee et al. Zhou et al. Yin et al.
Examples. Audio-visual speech enhancement with MEAD Dataset.
Initial video (with clean audio):
Noise level (SNR): 0 dB
A [PESQ: 2.29] B [PESQ: 2.19] C [PESQ: 2.42] D [PESQ: 2.28] E [PESQ: 2.09] F [PESQ: 2.49] G [PESQ: 2.51]
Noise level (SNR): -5 dB
A [PESQ: 1.61] B [PESQ: 1.43] C [PESQ: 1.79] D [PESQ: 1.69] E [PESQ: 1.56] F [PESQ: 1.95] G [PESQ: 1.99]
Reference:
A: Noisy speech (input),
B: Enhanced by audio-only VAE (Leglaive et al.),
C: Enhanced by CVAE (Sadeghi et al.),
D: Enhanced by Res-AV-CVAE-ST-GAN (Zhou et al.),
E: Enhanced by Res-AV-CVAE-DA-GAN (Yin et al.),
F: Enhanced by Res-AV-CVAE-RFF (Kang et al.),
G: Enhanced by Res-AV-CVAE-DFF (Proposed)




