HappyFeat – The software to ease BCI workflow in clinical applications
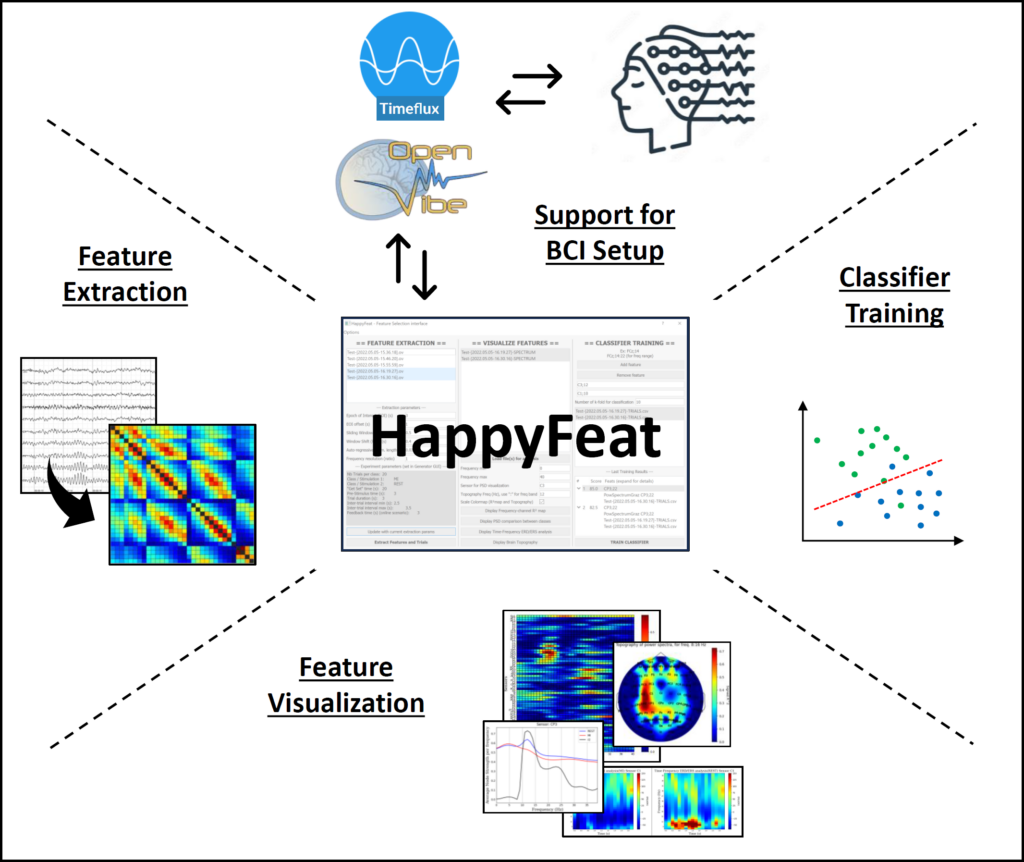
HappyFeat is an open-source Python software aiming to simplify the use of BCI pipelines in clinical settings, and help researchers introduce network and graph-based approaches in BCI, using features based on functional connectivity. It consists of Qt-based GUIs allowing to effortlessly extract classification features based on spectral power or connectivity, and select and combine them to train a BCI classifier. HappyFeat seamlessly interfaces with BCI softwares (i.e. OpenViBE), via automatic scenario generation and manipulation, to greatly reduce experimental setup complexity.
A Desbois, T Venot, F De Vico Fallani, M-C Corsi. HappyFeat—An interactive and efficient BCI framework for clinical applications. Software Impacts (2024) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpa.2023.100610. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2665963823001471)
Vizaj – A free online interactive software for visualizing spatial networks
Vizaj is an open-source 3D visualization tool for networks with fixed node position, based on Three.js. It is provided with a GUI which helps customizing the nodes, links background, support item, camera and any extra informations. The camera can be rotated by drag and drop. Right-click drag and drop translates the camera. Scrolling zooms and unzooms, etc.
T Rolland, F De Vico Fallani. Vizaj—A free online interactive software for visualizing spatial networks. Plos One (2023) https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0282181
The brain-computer interface multimodal platform
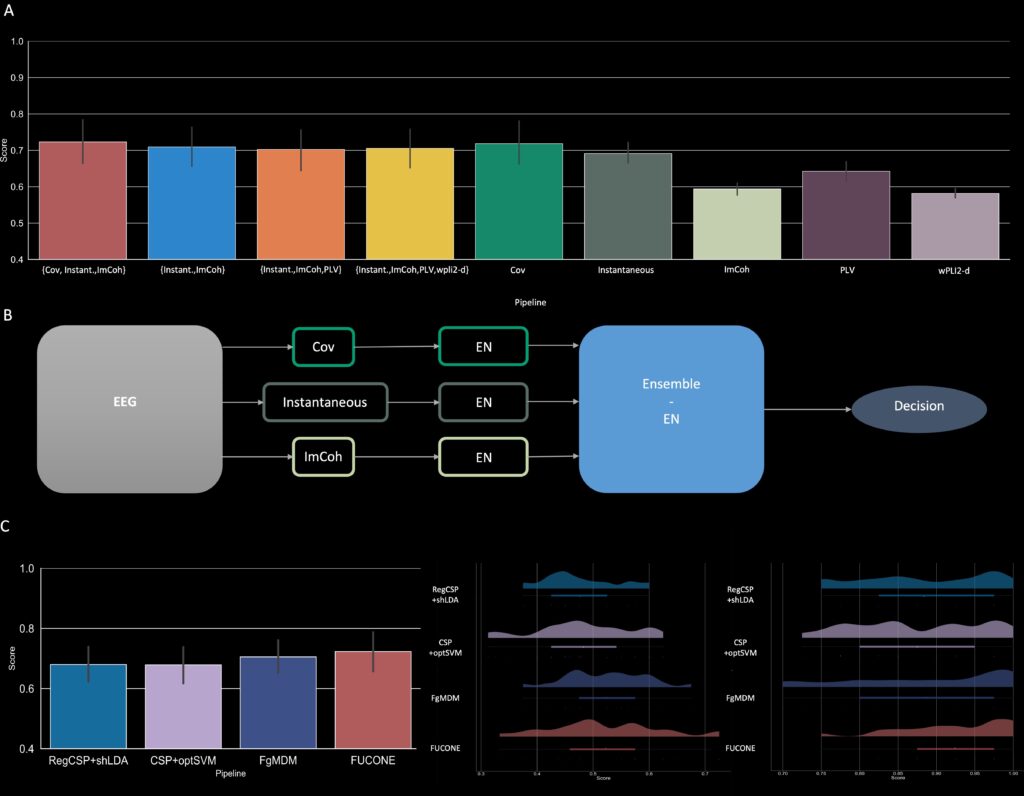
FUCONE – Functional connectivity ensemble method to enhance BCI performance
FUCONE combines functional connectivity and covariance within a Riemannian framework to increase the robustness of brain–computer interfaces classification. Associated publication:
Chevallier, S., Corsi, MC , Yger, F., & De Vico Fallani, F. (2022) Riemannian geometry for combining functional connectivity metrics and covariance in BCI. Software Impacts. doi:10.1016/j.simpa.2022.100254
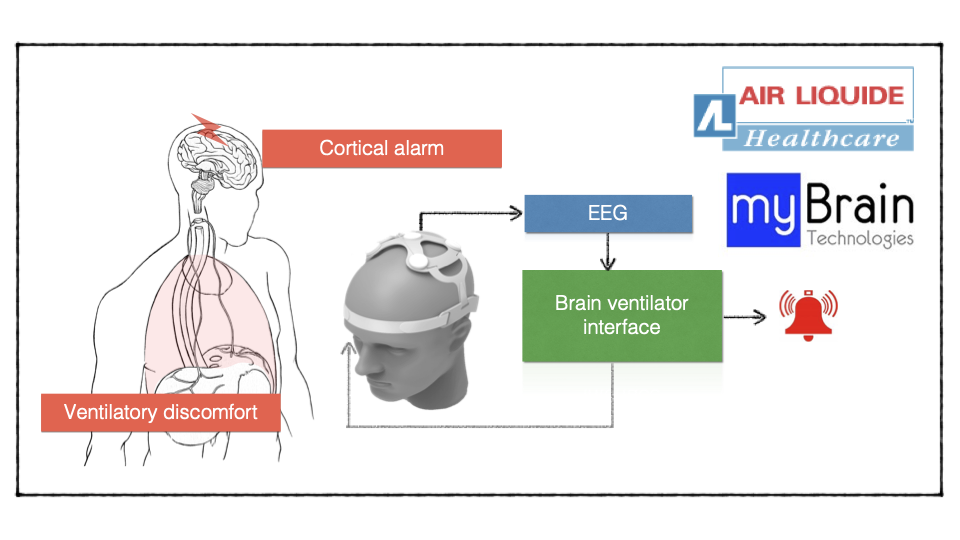
The Brain-Ventilator Interface – Online assessement of respiratory dyscomfort in sedated patients