PhD

- University of Yaoundé I, Cameroon, Dec. 2015-April 2021
- Title: Modelling, analysis and control of plantain plant-parasitic nematodes
- HAL: tel-03217816
- Supervisors: J. J. Tewa, S. Touzeau, F. Grognard
- Partners: CIRAD, Centre africain de recherches sur bananiers et plantains (CARBAP)
Context


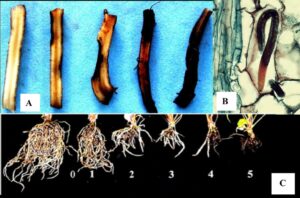
- Banana, including plantain: major staple food – Cameroon: 2% GDP
- Burrowing nematodes Radopholus similis
- develop, feed and reproduce in roots
- severe crop losses, up to banana toppling
- Control methods
- nematicides: harmful to environment and human health
- cropping practices based on soil sanitation, including fallows
- tolerant or resistant banana varieties
Objectives
- Develop a model describing plant-parasitic nematode damages in a plantation
- Design efficient and sustainable control strategies to limit damages, based on fallows
Results
Seasonal banana-nematode interaction model
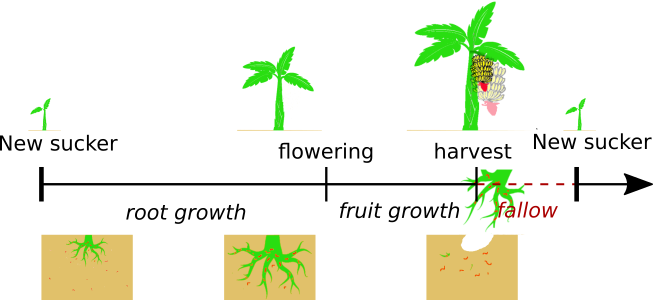
- Hybrid system to describe plant growth: roots only grow until flowering; plant replaced either by a lateral shoot, or by a new sucker at the end of each cropping season
- Yield proxy based on healthy roots
- Model analysis assuming fast root infestation dynamics
- Conditions on pesticide load or fallow to ensure nematode extinction
I. Tankam Chedjou, S. Touzeau, F. Grognard, L. Mailleret, J.-J. Tewa. A multi-seasonal model of the dynamics of banana plant-parasitic nematodes. In: CARI’2018 – 14th African Conference on Research in Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2018. HAL: hal-01871510v1
I. Tankam Chedjou, S. Touzeau, L. Mailleret, J.-J. Tewa, F. Grognard. Modelling and control of a banana soilborne pest in a multi-seasonal framework. Mathematical Biosciences 322:108324, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2020.108324. HAL: hal-02775460
Optimisation of fallow deployment
- Agricultural control: constant or variable fallow periods, which reduce the nematode population in the soil (no host to feed and reproduce)
- Aim: maximise the cumulated yield (reduced by the nematode population), while minimising the costs of nursery-bought pest-free suckers, on a fixed time horizon that lasts several cropping seasons
- Systematic use of pest-free suckers and fallows between two cropping seasons
I. Tankam Chedjou, F. Grognard, J.-J. Tewa, S. Touzeau. Optimal and sustainable management of a soilborne banana pest. Applied Mathematics and Computation 397:125883, 2021. DOI: 110.1016/j.amc.2020.125883. arXiv 2020: 2007.12606. HAL: hal-03111065
- Occasional use of pest-free suckers and fallows to reduce costs; otherwise lateral shoot kept after plant uprooting for the next cropping season
I. Tankam Chedjou, F. Grognard, J.-J. Tewa, S. Touzeau. When and how to fallow: first steps towards banana crop yield improvement through optimal and sustainable control of a soilborne pest. Journal of Interdisciplinary Methodologies and Issues in Science, Digital Agriculture in Africa, 2021. DOI: 10.18713/JIMIS-120221-8-4. HAL: hal-03103785
Misc
- EPITAG visits in France
- Sep.-Dec. 2017
- April-Aug. 2018
- Feb-June 2019 (EMS-Simons grant)
- Conferences
- ECMTB 2018, Lisbon, Portugal – HAL: hal-01859995
- CARI’2018, Stellenbosch, South Africa – HAL: hal-01871510
- BIOMATH 2019, Bedlewo, Poland – HAL: hal-02139560
- CMPD5 2019, Fort Lauderdale, USA. HAL: hal-02139546
- EMS-Simons for Africa grant, 2018
- Ovide Arino Outreach Award, joint ESMTB and SFBT prize, 2021
- Career after PhD
- Postdoc, WAVE Center, Abidjan, Ivory Coast & Chris Gilligan’s Epidemiology and Modelling Group, University of Cambridge, UK, 2022 (Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation funding)
- Postdoc, IGEPP, INRAE Rennes, France, 2023-2024 (EU and regional Bienvenüe funding)

