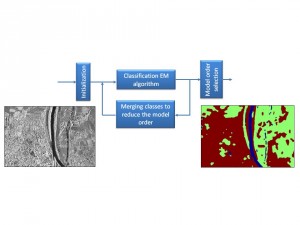
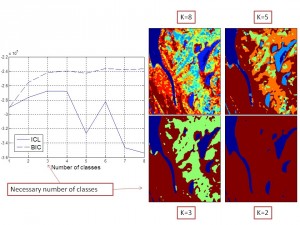
Remote Sensing:
-
High-resolution SAR image classification. Left: (up) Original optical acquisition of the city of Port au Prince, Haiti (copyright GeoEye, 2010) and (down) coregistered COSMO-SkyMed SAR image (copyright ASI, 2010). Right: Classification obtained with a hierarchical Markovian method based on a quad-tree applied to the multi-sensor dataset. Five classes are considered for this dataset: water (in blue), urban areas (in red), low vegetation (in green), sand (in yellow) and containers (in purple).
-
Region-based classification of a TerraSAR-X image by hierarchical agglomeration based unsupervised algorithm. The TerraSAR-X image was acquired over the city of Rosenheim in Germany. Copyright Infoterra.
-
Region-based classification of a TerraSAR-X image by hierarchical agglomeration based unsupervised algorithm. The TerraSAR-X image was acquired over the city of Sanchagang in China. Copyright Infoterra.
-
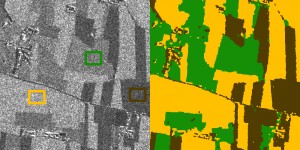
SAR image of field area (with learning areas in rectangles) of Piemonte, Italy (COSMO-SkyMed, copyright ASI, 2008), 1000×1000 pixels, and supervised field classification results obtained by the Generalized Gamma Distribution with parameters estimated by the Method of Logarithmic Cumulants.
-
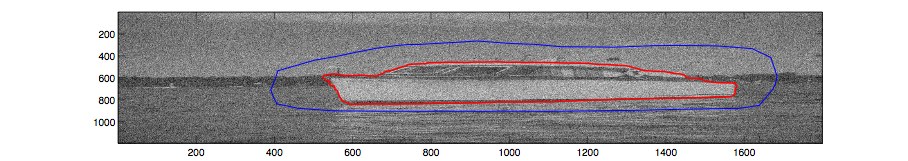
Automatic detection of a target object (here a boat) in a noisy image using the Higher Order Active Contour (HOAC) framework.
-
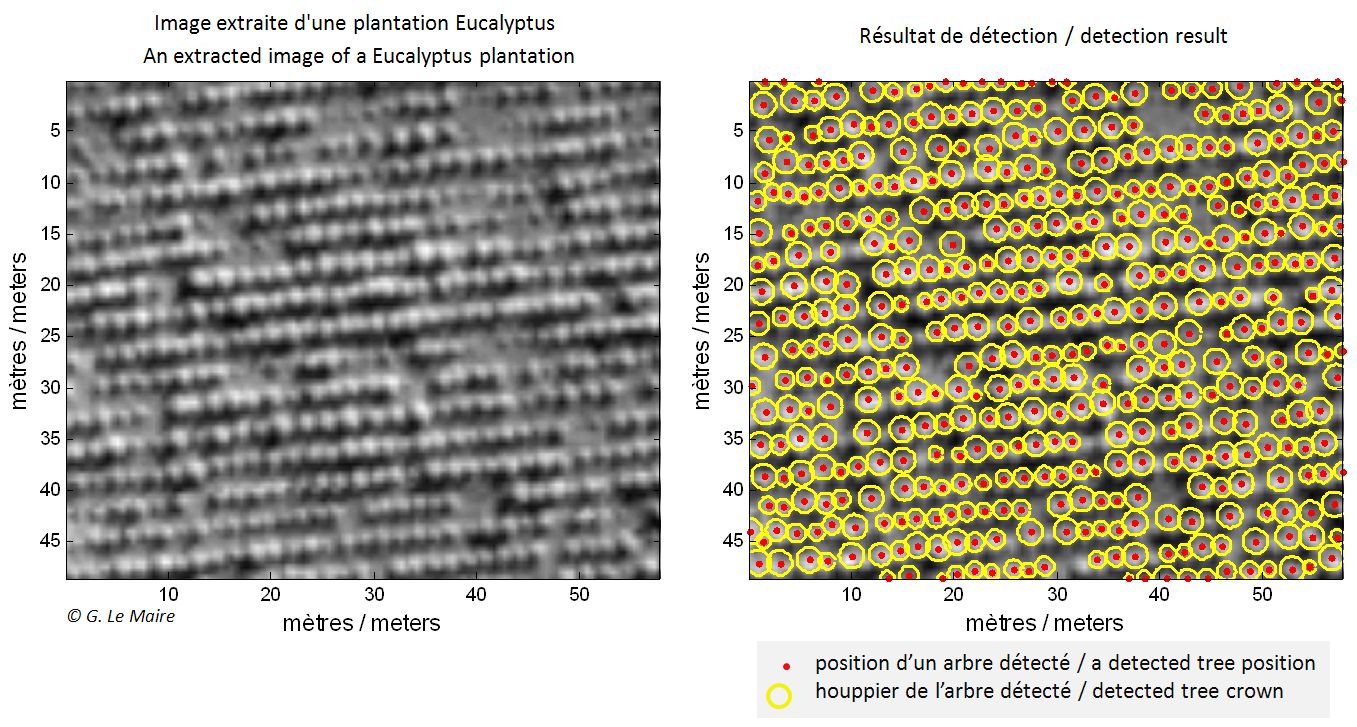
Tree-crown detection in a Eucalyptus plantation using marked point process modeling. Copyright CIRAD/IRD/INRIA.
-
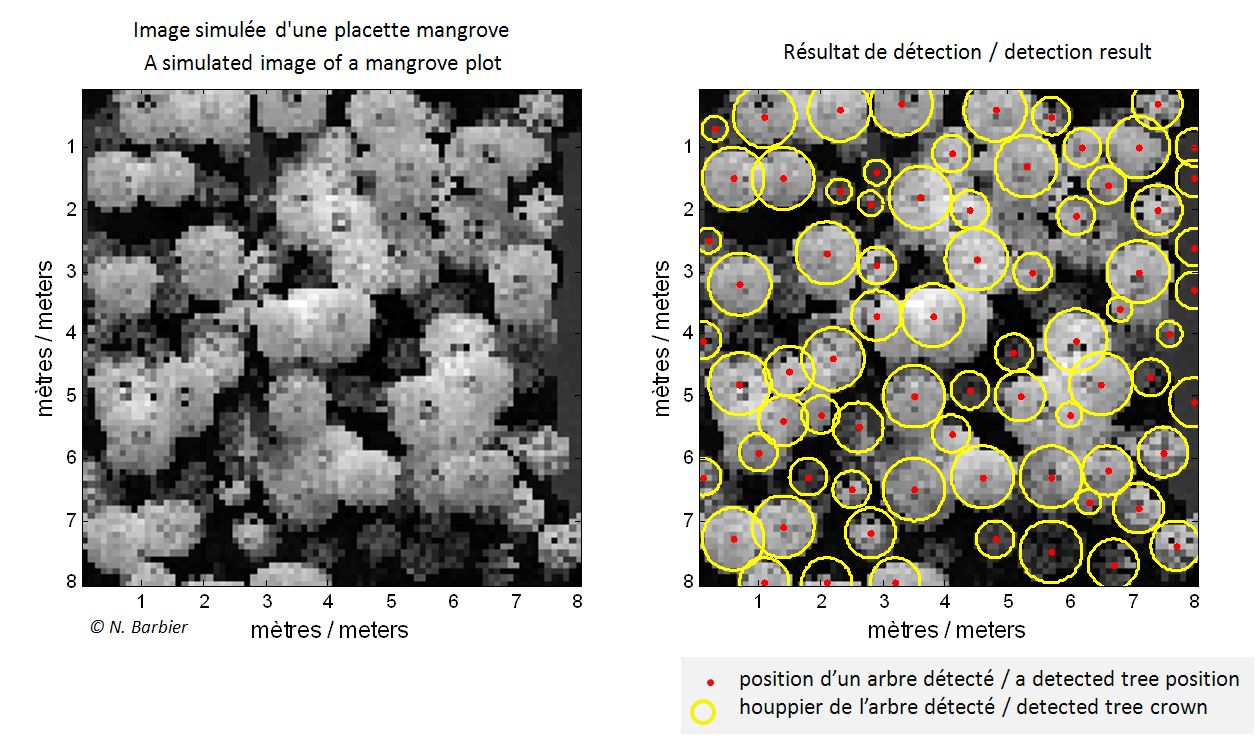
Tree-crown counting in a mangrove plot using marked point process modeling. Copyright IRD/INRIA.
Skincare:
-
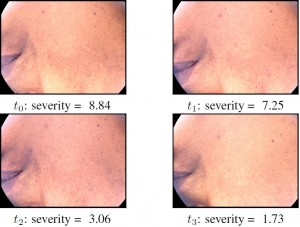
Melasma: Time measurement of severity by a spectral criterion of contrast. Copyright Galderma/INRIA.
-
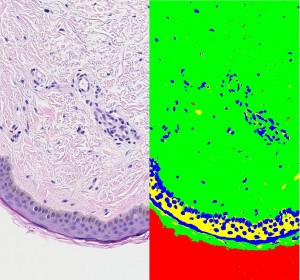
Histological image classification of the skin. Copyright Galderma/INRIA. Left: Original red, green, blue (RGB) histological image. Right: Classification results obtained with a hierarchical Markovian model based on a quad-tree.
This image is classified into four classes that were interpreted as the cytoplasm (in yellow in the classification maps), the nuclei (in blue) and the background (in red). The green class gathers the dermis matrix, the collagen and the stratum corneum keratin. -
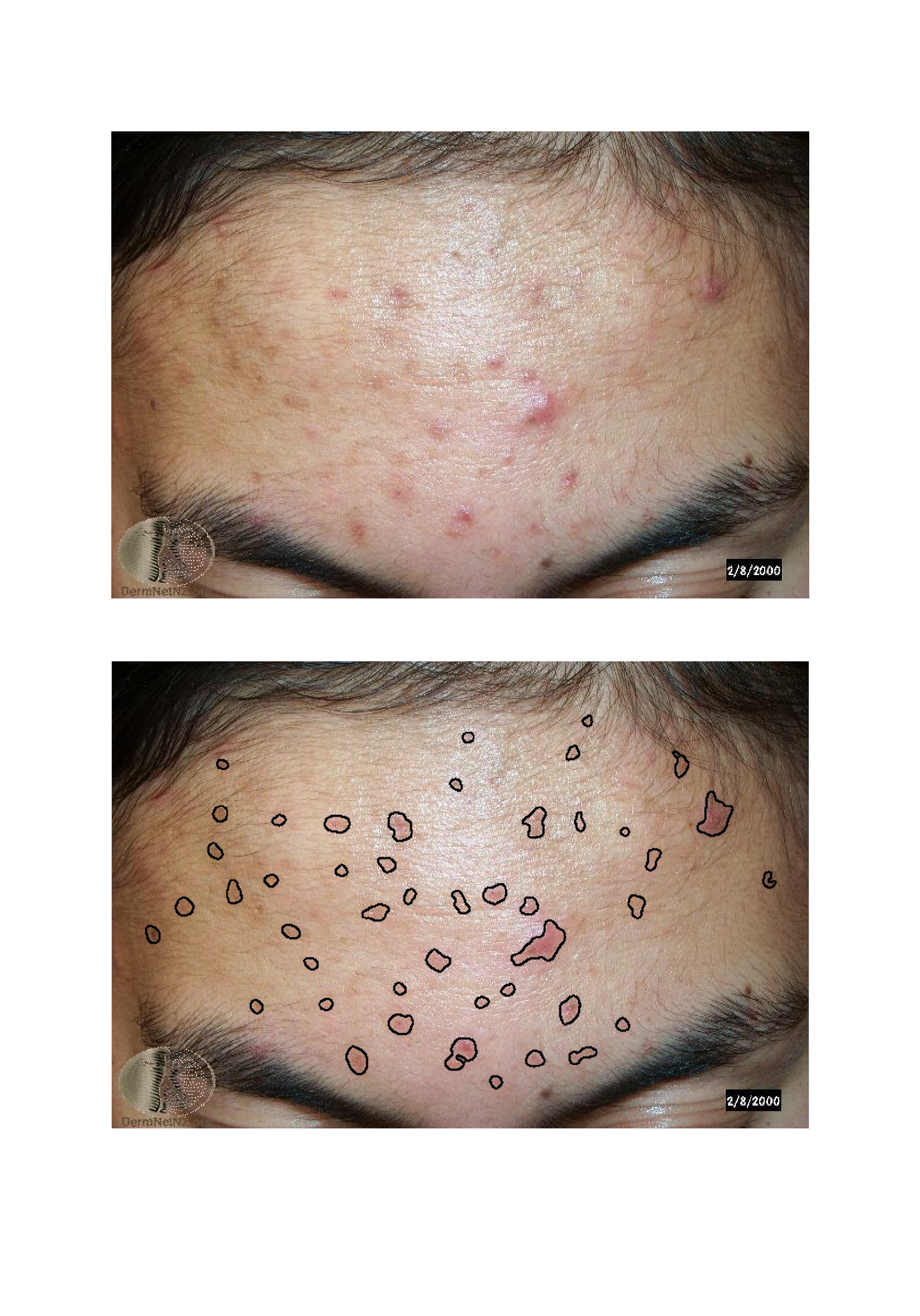
Acne detection in conventional RGB image with artifacts of highlights and shadows. Upper image: RGB acne image from public dataset of Dermnet NZ (http://www.dermnetnz.org/). Lower image: acne segmentation result. This study is conducted within LIRA Consortium, Copyright AYIN/INRIA.