EIT-ICT Lab
EIT-ICT Lab
Indoor Activity Monitoring at Nice Hospital
Inria
Motivation
To build an innovative framework for modeling activities of daily living (ADLs) at the site for helping the doctors in accurately assessing the patient for Alzheimer’s disease.
More specifically, the project aims:
- to assess the initiative ability of patient and whether the patient is involved in goal directed behaviors
- to assess walking disorders and potential risk of falls.
The older people population is expected to grow dramatically over the next 20 years. The number of people requiring care will grow accordingly (including in particular Alzheimer patients), while the number of people able to provide care will decrease.
Without receiving sufficient care, elderly are at risk of loosing their independence. In recognition of this position of elderly in the near future, this project aims at building an innovative framework for modeling activities of daily living (ADLs).
To differentiate early stage Alzheimer’s disease from control participant using actigraph and audio-video data analysis obtained during the completion of a standardized scenario of daily living oriented activities.
- Differentiate early stage Alzheimer’s disease patients or related disorder with patients with mild to moderate stage of the disease.
- To assess the impact of behavioral disturbances and apathy in particular on the completion of the proposed activities of daily living.
- To assess the impact of cognitive decline on speaking behavior and voice sound characteristics
- To assess the adjunct feasibility of the actigraph coupled with audio-video setting to normal memory consultation.
- Estimate the acceptability of this evaluation method by the participant during a standard consultation in a memory center
- To assess the participant acceptability to introduce a follow-up monitoring system based on the use of ICT within their own house
This project focuses on Alzheimer disease patients in early stage and dealing mainly with “technology assessment” and “preventative care” that takes account of medical, physical and mental states to safeguard an individual and intervene/warn before “crisis intervention” is required.
For this purpose, this project:
- collect and combine multi-sensor information to detect activities and assess behavioral trends to provide user services at different levels.
- create an experimental room of the Nice University hospital./p>
Experimentation
The clinical part of the project study was conducted in the Nice Memory Center, located in the geriatric department of Nice’s university hospital.
An observation room was equipped with everyday objects for use in ADLs and IADLs, e.g. an armchair, a table, a coffee corner, a TV, a PC, and a library. Two fixed monocular video cameras (8 frames/seconds) were installed in order to capture the activity of the participants.
Scenario
The overall aim of the clinical scenario is to enable the participants to undertake a set of daily tasks that could realistically be achieved in the setting of the observation room.
The first scenario was divided in three parts covering basic to more complex goal directed activities :
- Directed activities : the aim of this part of the assessment was to identify characteristics of gait and walk parameters in activities with limited implication of cognitive capacities. This part was based on the short physical performance battery (SPPB) and required the examiner, who remained in the room, to verbally direct the participant to undertake various daily tasks. The examiner also scored the performance.
- A semi-directed part : the subject stayed alone in the room, with a list of tasks to accomplish (activities of daily living : read newspapers, make some tea, use the phone, watch the TV, take his pills, write the shopping list, …)
- A free part : the subject stayed alone in the room for 30 minutes, he can do anything he wants (except destroying the room…)
Ethical Issues
Consent
Nurse will explain patient and the family care taker of the patient about
- the tasks to be performed
- purpose of the experimentation’s
Consent from the patient and the family care taker will be taken to conduct the experimentation.
Each clinical study is submitted to the Nice Ethical committee.
Each clinical study include a standard clinical assessment and an “ecological scenario”
Ethical Board (CPP)
This is a local ethical body with 2 external reviewers. This document explains about the experiments, done on the patients, few months before it is actually conducted on the patients. This local body includes people from different background like social workers, internal doctors, 2 external doctors and representatives from association of older people. Feedback from this committee is taken and need to get the approval.
Agency for personal data protection (CNIL)
This is a national ethical committee. This is an agency which approves the usage of the information/content and database. This is a very important aspect since the database contains information about people/patients. Once this is accepted and approved, this can be submitted to European level ethical committee (Data Controller).
Partners
The Nice University Hospital (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice – CHUN) is a public health body, regulated by a public board, with activities over five sites including four hospitals and a reeducation centre (2284 beds and employing 6183 professionals including 824 doctors).
CHUN is involved in several eHealth projects aiming at designing the « wall-less » hospital of the future (technological innovation unit pole which aims at applying information technologies to the healthcare domain) and is an active partner in the French Competitiveness Pole “Secured Communication Solutions”.
As part of the CHUN, The Memory Center (Centre Mémoire de Ressources et de Recherche) is conducting evaluation of memory disorders, as well as clinical and research activities in collaboration with geriatry, neurology and psychiatric departments.
CHUN is the leader of the Sweet Home Project, in charge of coordination, medical expertise on elderly, cognitive impairment and behavioral disorders, and experimentation in the Nice hospital.
Inria is a French public-sector scientific and technological institute operating under the dual authority of the Ministry of Research and the Ministry of Industry.
The Stars team is a multi-disciplinary Inria research team working at the frontier of computer vision, knowledge based systems, and software engineering.
The Pulsar team has participated in more than 20 research projects and has managed to recognize a large variety of scenarios in different applications: fighting, abandoned luggage, graffiti, fraud, crowd behavior in metro stations, on roads and onboard trains, aircraft arrival, aircraft refueling, luggage loading/unloading on airport aprons, bank attack, office behavior for ambient intelligence, access control in buildings and wasp monitoring for biological application.

MICA Center (Multimedia, Information, Communications and Applications) is an international unit of the CNRS (UMI 2954) established in Hanoi, Vietnam. It has been founded at the beginning of 2002 to participate to the development of the information technologies in Vietnam and to satisfy preoccupations concerning their evolution.
The studies realized in MICA Centre aim to research and develop theoretical results and applications in the following topics: processing complex signals (speech and images), multimedia applications, human-machine interfaces, perceptive spaces and ubiquitous computing, advanced (virtual, embedded and distributed) instrumentation. The main research topic of MICA Centre concerns speech processing in Vietnamese language, a field in which it has become the most important research laboratory in Vietnam.
Numerous research projects were developed by MICA researchers in close cooperation with French laboratories and laboratories from neighbour countries. As an UMI of CNRS, MICA Center takes an active part in the international visibility of CNRS, and more generally of French research, in a world area where are imagined, designed and diffused a great number
of scientific and technological innovations in telephony, multimedia and information technologies fields.
MICA researchers already participated to several (national or international) research project related to pervasive environments and ubiquitous computing (SIAM project, “Smart Campus” project, ISERE project,”Smart ECG” project).

The SMILE Lab (Smart Media in Intelligent Living Excellence), in the Department of Electrical Engineering of National Cheng Kung University (NCKU), Taiwan, is devoted on computational intelligence, image and video analysis, pattern recognition and computer vision for seventeen years. Particularly it applies most of the techniques on healthcare applications and has long time cooperation with hospitals or healthcare centers.
SMILE Lab has conducted more than 20 projects, some of which are national scale projects.
These national scale projects include :
- the development of home gateway and event detection from video sequences to set up an integrated environment for the elderly, his/her care takers, and his/her children,
- the development through the integration of RFID, wireless sensor networks and multimedia analysis for psychiatric patient monitor,
- Healthcare center event detection through video sequences.
Recently it has developed video analysis techniques for human daily behaviour understanding, walking style analysis and abnormality detection. These results are also combined and fused with other media analysis and through the integration of wireless sensor networks, applied for the improvement of healthcare, especially for homecare or care centers. It also conducted the research of target tracking and behaviour analysis through multicamera fusion.
In the Sweet Home Project, SMILE Lab participate on video analysis and sensor signal analysis from low level feature analysis to high level semantic understanding, particularly through the integration of multi-camera and multi-modal outputs for detecting the early signs of Alzheimer patients from their daily behaviors.

National Cheng Kung University Hospital is located in Tainan City, Taiwan. NCKUH began its running in 1988 and became soon as one of the best national medical centers in Taiwan. NCKUH has more than 1000 beds.
Division of Behavioural Neurology belongs to Department of Neurology and is one of the best divisions pertaining to this field in Taiwan. Before his being the head, Dr. Pai initiated a dementia clinic in NCKUH in 1994 and over the past months 800 patients with dementia in average have their regular follow-ups in the clinic.
In NCKUH, an ADRC was open in 2006, which consists of neurologists, neurosurgeons, psychiatrists, psychologists, pathologists, nurses, and related professionals. In NCKUH, we have CT, MRI, SPECT, and PET. Room for Neuropsychologal tests is located in the 9th floor of NCKUH and many batteries and tests can be conducted, such as MMSE, CASI, NPI, CDR, ADAS-cog, BEHAVE-AD, and many experimentally oriented cognitive tests. In the same way, Dr. Pai’s team had participated in many multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials on patients with varied kinds of dementias.
Moreover, Dr Pai has been the president of Zeelandia Dementia Association (established in 2004). Up to 2008, a total of 325 members are enrolled. Zeelandia is the old name of Tainan City and ZDA is the first local dementia association in Taiwan. ZDA had been a very important dementia support group which interacts closely with NCKUH reciprocally.
Method and Site
Method: Event Recognition Platform
- Video/ audio Sensors
- Inertial Sensors
Site: Nice-HOSPITAL, Nice
Observed People and duration
It is a non-randomized multicentric study involving 3 kinds of participants:
- Young age group: (n=50)
- Control Group: non Alzheimer (n=50)
- Pre-dementia / MCI Patients group : n =50
- Dementia patient group : n=50.
- Following are the course of the study:
- Inclusion period= 9 months
- Data analysis =3 months
- Length of the study = 12 months
- Duration of the visit= 2 to 3 hours with 25 minutes in the experimental room.
Based on the previous data obtained from the pilot study, we have determined an autonomy score (range from 0 to 1) with a mean for each patient group of 0.5 for the patients with dementia, 0.6 for the prodromal and 0.7 for the control respectively.
This score is based on the total duration time during which the participant is showing activities aim-oriented and a composite score of how the participants plan and complete the predefined actions.
The within group error tolerance is 0.1 and a sample of 111 patients will allow to produce an effect size F of 0.3 (0.1=low; 0.25=medium, 0.4= large) with a power of 90% and alpha set at 0.05. The critical size for each group is 36 subjects.
In consideration of the critical size and the eventuality of data corruption, we will include 50 patients for each group for a total sample size of 150 patients.
Sensors
Video cameras : a camera captures the whole room, so we can follow any activity in it. The recordings are then processed by the INRIA algorithms, and can be used as “ground truth”.
Microphones : a microphone records the sound in the room. Recordings are then processed by MICA algorithms.
Actimeters : The subject has to wear the “MotionPod” sensor on his thorax (with an elastic band). This device car record an “activity index” for each second, as well as the posture (lying, sitting, standing, walking).
ECG sensor : The subject is also wearing the “VeryLife” sensor, recording his electrocardiogram. With those data we can assess the stress level during each stage of the scenario.
|
Expected measurements & data (Observation period of collected data) |
Required Sensor |
(Obs. period: mono task walking activity/dual task) |
|
(obs. period: mono task walking activity/dual task) |
|
(obs. period: mono task walking activity/dual task) |
|
(obs. period: mono task walking activity/dual task) |
|
(obs. period: mono task walking activity/dual task) |
|
|
|
Software Processing
Input video streams and theground truth is required to accomplish the below.
People Detection and Tracking
Detection of the patients in the video stream is the primary aspect and tracking the person is the next important aspect in assessing. The detection and tracking is performed using respective algorithms developed by us using HOG and LBP for example.
Event Recognition
The proposed automatic video monitoring system takes as input video streams and a Prior knowledge for 3D scene modeling and events to recognize. The system contains a vision component (e.g. detection, classification and tracking processes) and an event recognition component. The vision component allows detecting people and tracking their different movements over the time in the scene. The event recognition component allows recognizing temporal and spatial events, and posture associated with the tracked person.
Processing chain
Database
If you would like to have access to the recorded data, please download and fill the form in the link below (double click) and send it back to us.
Data Format
Assessment of Activities:
- Location
- Duration
- Activities
- Experimental Conditions
- Sensors Included
- Expected measurements and data
Evaluation and Results
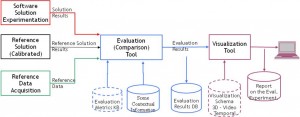
At Inria, an evaluation framework has been developed to assess the performance of Gerontechnologies and Video surveillance. This framework aims at better understanding the added values of new technologies for home-care monitoring and other services. This platform is available to the scientific community and contains a set of metrics to evaluate automatically the performance of software given some ground-truth.
Description
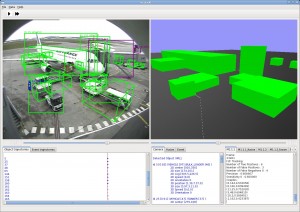
The software ViSEvAl (ViSualisation and EvAluation) provides a GUI interface to visualize results of video processing algorithms (such as detection of object of interest, tracking or event recognition). Moreover this software can compute metrics to evaluate specific tasks (such as detection, classification, tracking or event recognition). The software is composed of two binaries (ViSEvAlGUI and ViSEvAlEvaluation), and several plug-ins. The users can add their own plug-ins to define a new metric for instance.
ViSEvAl is under GNU Affero General Public License (AGPL)
Interface
Evaluation Platform
States:
Inside zone of interest (coffee corner, office zone, reading table zone, phone table, plant zone, pharmacy zone)
Actions/Activities:
- Having news paper in the hand
- Having remote control in the hand
- TV turning on<
- TV turning off
- Having watering can in the hand
- Pouring water on the plant
- Tea kettle turning on
- Pouring water in the tea cup
- Having the phone on the hand
- Composing phone number
- Catching (prescription/drugs can) in the drug box
- Putting away (prescription/drugs can) in the drug box
- Selecting drugs
- Putting drugs into the pillular
- Writing shopping list
- Paying Electricity bill
Publications
Automatic Video Monitoring system for assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease symptoms
Romdhane R., Mulin E., Derreumaux A., Zouba N., Piano J., Lee JH., Leroi I., Malléa P., David R., Thonnat M., Brémond F., Robert PH.
JNHA, in press
Sensors data assessment for older person activity analysis.
Proceedings of the ISG*ISARC 2012 Conference (International Society for Gerontechnology, the 8th world conference in cooperation with the ISARC, International Symposium of Automation and Robotics in Construction), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 26 to 29 June 2012.
C. Crispim-Junior, V. Joumier, Y.L. Hsu, M.C. Pai, P.C Chung, A. Dechamps, P. Robert and F. Bremond.
Video Activity Recognition Framework for assessing motor behavioural disorders in Alzheimer Disease Patients.
International Workshop on Behaviour Analysis, Behave 2011, Sophia Antipolis, France on the 23rd of September 2011.
J. Joumier, R. Romdhane, F. Bremond, M. Thonnat, E. Mulin, P.H. Robert, A. Derreumeaux, J. Piano and L. Lee.
Probabilistic Recognition of Complex Event.
8th International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, ICVS 2011, Sophia Antipolis, France on the 20th-22nd of September 2011.
R. Romdhane, B. Boulay, F. Bremond and M. Thonnat.
Communications
Clinical assessment using information and communication technologies in Alzheimer disease : Interest for clinical trials
Robert P.H., Romdhane R., Bremond F.
3rd Conference Clinical trials on Alzheimer’s disease. November 3-5, 2010, Toulouse. JNHA, 2010, vol 14, suppl 2, O15, S9
Etude comparative des techniques actigraphiques et vidéo d’étude de l’activité motrice chez 3 sujets dans le cadre d’un travail préliminaire de développement d’outils d’évaluation objective de l’apathie
Robert P.H., Mulin E., Piano J., Derreumaux A., Malléa P., David R.
Congrès Français de Psychiatrie, à Nice, les 2, 3, 4 et 5 décembre 2009
Intérêt des gérontechnologies dans la mesure de l’apathie chez les patients atteints de maladie d’Alzheimer
Mulin E., Romdhane R., David R., Lee J., Zouba N., Piano J., Derreumaux A., Brémond F., Robert P.H.
CIFGG, Nice, Octobre 2010
Les objets communicants pour un futur plus autonome. Où en est-on de l’usage de l’actimétrie dans le domaine des troubles du comportement ?
Mulin E., Robert PH.
CIFGG, Octobre 2010
Utilisation d’un système de monitorage vidéo pour l’étude de l’apathie chez les patients présentant un déclin cognitif léger
Mulin E, Romdhane R, David R, Lee J.H, Piano J, Zouba N, Thonnat M , Bremond F, Leroy I, Robert P.H.
Unités de soins Alzheimer, PARIS, décembre 2010
Automatic Video Monitoring System To Detect Apathy in Mild Cognitive Impairment
Mulin E.
Annual Meeting Ressource of American Academy of Neurology, à Hawaï, poster présenté le 12 Avril 2011
Apathie précoce : intérêt des nouvelles technologies
E. Mulin, P.H. Robert
XXIVe GRAL, à Marseille, le 28 janvier 2011, communication orale
Intérêt de l’analyse vidéo dans l’étude des troubles du comportement dans la maladie d’Alzheimer: étude préliminaire
E. Mulin, J. H. Lee, J. Piano, P.H. Robert
Congrès national des Unités de soins, d’évaluation et de prise en charge Alzheimer 2010, les 16 et 17 décembre 2010
Utilisation des technologies de l’information et de la communication dans l’évaluation des troubles du comportement
F. Bremond, E. Mulin
Réunion de la fédération des CMRR du sud de la France, les 4 et 5 février 2011, à Paris
Symposium organization at the 15th IPA
International Psychogeriatric Association congress – La Hague 6 – 9 september 2011
Symposium title: New technologies applications for behavioral and Activities of daily living
I Leroi (UK)
Targeting the behavioural and cognitive domains: lessons from Parkinson and Alzheimer’s disease
F Bremond (France)
GERHOME and SWEET Home: the methodological aspect of an automatic video monitoring system
E Mulin (France)
SWEET Home: Automatic video monitoring system for the assessment of BPSD and autonomy in Alzheimer’s Disease
J Yesavage (USA)
Advanced techniques of sleep monitoring and genetic analyses in the study of cognitive problems of older adults
R David (France)
Relation between genetic analysis and actigraphy for the assessment of apathy in AD
Meeting reports
- SWEET HOME Partner meeting ; November 9, 2010
- SWEET HOME Partner meeting ; December 21, 2010