Imaging-psychatry challenge (IMPAC): predicting autism
The IMaging-PsychAtry Challenge (IMPAC) is a data challenge on Autism Sprectrum Disorder (ASD). ASD is a severe psychiatric disorder that affects 1 in 166 children.
There is evidence that ASD is reflected in individuals brain networks and anatomy. Yet, it remains unclear how systematic these effects are, and how large is their predictive remain unclear. The large cohort assembled here can bring some answers. Predicting autism from brain imaging will provide biomarkers and shed some light on the mechanisms of the pathology.
Deriving reproducible biomarkers from multi-site resting-state data: An Autism-based example
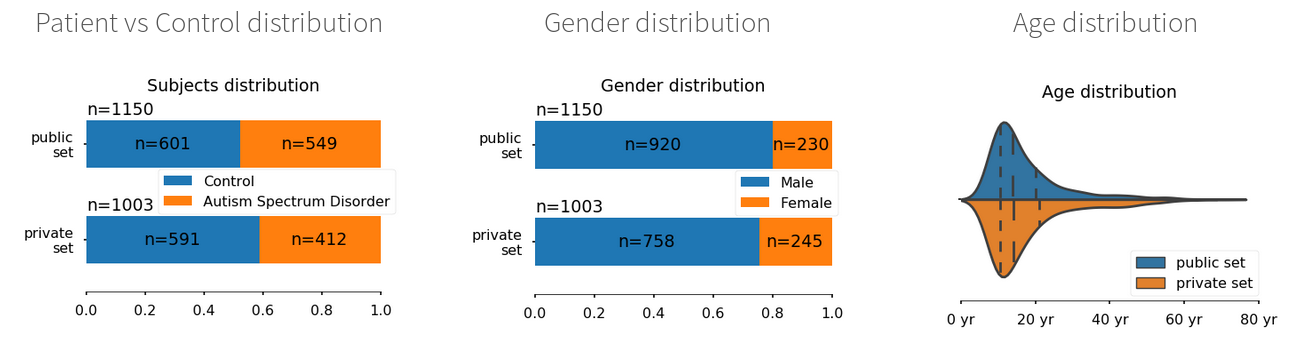
Here we demonstrate the feasibility of inter-site classification of neuropsychiatric status from functional connectivity, with an application to the Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE) database, a large (N=871) multi-site autism dataset. We predict this neuropsychiatric status for participants from the same acquisition sites or different, unseen, ones. Prediction accuracy improves as we include more subjects, up to the maximum amount of subjects available.
Comparing functional connectivity based predictive models across datasets
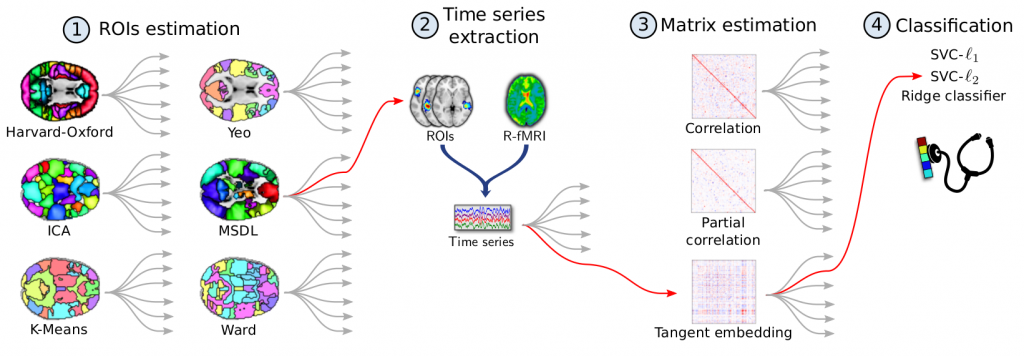
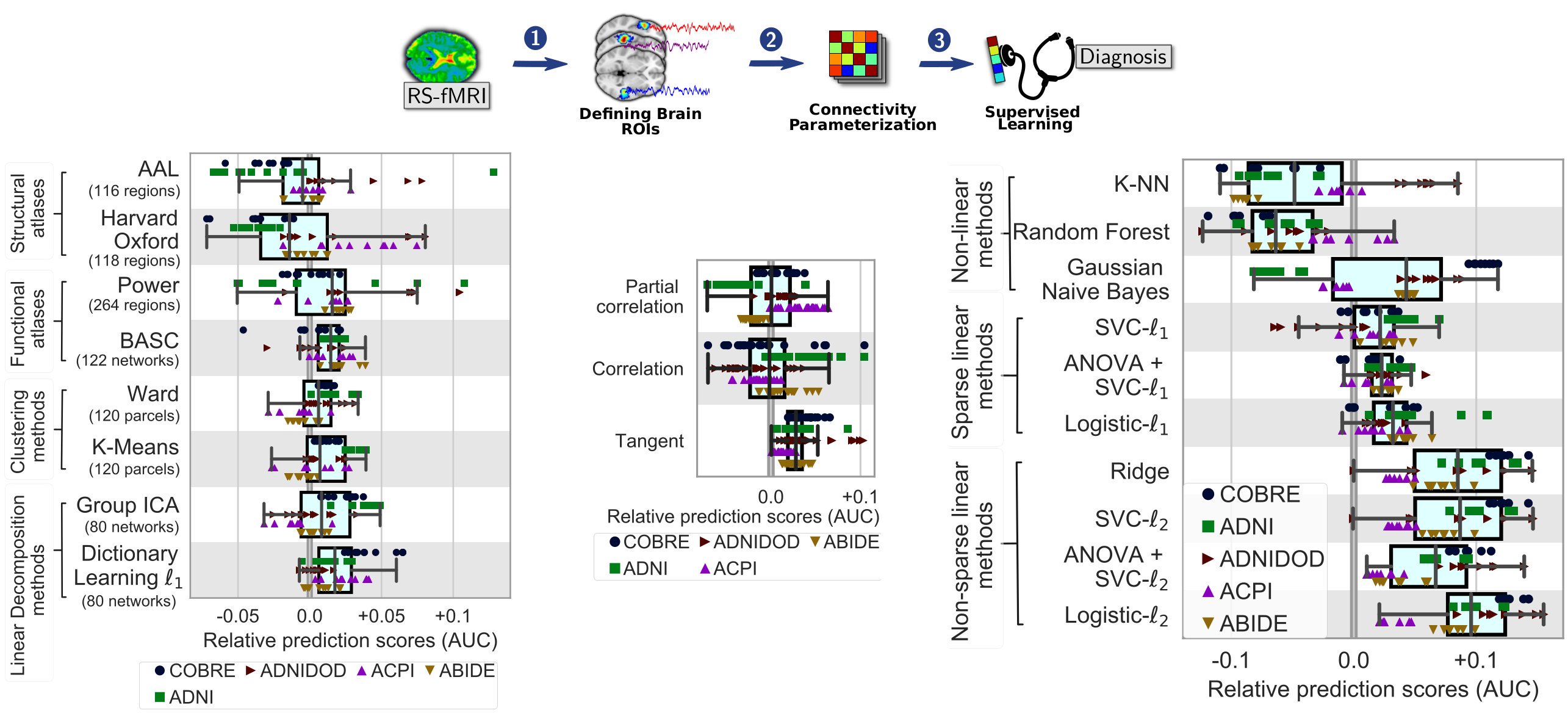
Here we systematically study resting state functional-connectivity (FC)-based prediction across six different cohorts (ADNI, COBRE, ACPI, ADNIDOD, ABIDE, HCP), a total of 2000 individuals. We explore various methodological choices: ROI set selection, FC metrics, and non-linear and linear classifiers to compare and evaluate the dominant strategies for the sake of prediction accuracy. We observe that: (i) tangent embedding performs better than correlation or partial correlation in all datasets; (ii) l2 regularized classifiers SVC and Ridge are more accurate than SVC- l1 classifier; (iii) with regards to brain atlases, decomposition methods (ICA, DictLearn) are generally the best choices, though with striking cross-datasets differences.