Our research
The amount of information available on the web today, and the fast rate with which new information appears, overwhelm most users. The goal of our research is to assist Web users in discovering content. One of the most powerful means today to help people discover new web content is sharing between members of online communities. In the case of communities of a place (e.g., people who live, study, or work together) people share common interests, but often fail to actively share content. To address this problem, we have developed WeBrowse, a passive crowdsourced content discovery system for communities of a place.
How WeBrowse Works
WeBrowse leverages the passive observation of web-clicks (i.e., the URLs users intentionally visit) as an indication of users’ interest in a piece of content. Intuitively, the more users click on a URL, the higher the interest in the content on the corresponding page. Our approach is then to leverage the collective clicks in a community to automatically discover relevant content to promote to users of the community.
To implement passive crowdsourcing, one must be in a position to observe the aggregated web-clicks of the community. Luckily, in many communities of a place, users will connect to the Internet from the same network, such as, e.g., the campus/enterprise network or the network of a residential Internet Service Provider (ISP) in a neighborhood. WeBrowse (i) observes web packets flowing through a network link, (ii) passively extracts HTTP logs (i.e., streams recording the headers of HTTP requests), and (iii) detects and decides on-the-fly the set of URLs to show to users.
Collected data
WeBrowse reads all HTTP (or un-encrypted Web) packets passing through the link that connects the Inria Paris network to the Internet to extract:
- The URL pointing to the requested object
- The “referrer field” pointing to the last visited page
- “User-Agent field” indicating the browser
- The anonymized IP address to distinguish between different users
We store anonymized traces in a secure server at Inria Paris. Access to the data is limited to the researchers listed in contacts.
Protecting Privacy
We understand that WeBrowse could potentially learn sensitive information about users in the Inria Paris network, so we take a number of steps to protect users privacy:
- All IP addresses are anonymized. We append a random numeric value to the address and we apply a hash function. After applying the hashing function it’s not possible to infer the original IP address.
- Eliminate URL parameters. Some URLs contain parameters to explicit the preferences of the user e.g. www.example.com?pref=red. We eliminate such parameters obtaining the original URL e.g. www.example.com.
- K-anonymity privacy. WeBrowse shows only content viewed by many users. This guarantees that is not possible to infer which particular user visited a content.
- Blacklist filtering. We maintain a list of URLs that are inappropriate. Users can repost URLs to be added to such list.
How to opt out?
As any crowdsourcing system, the more users contribute to WeBrowse, the better it works. However if you prefer not to participate you can opt out.
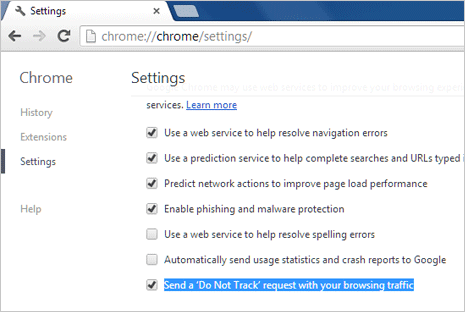
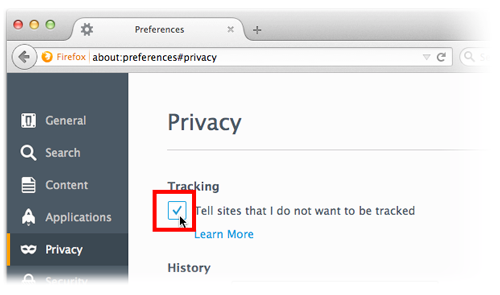
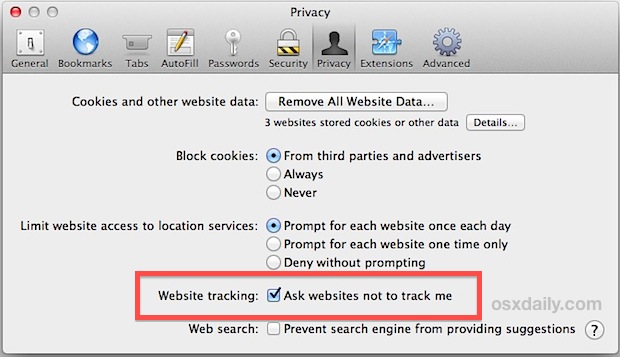
Opting out is simple, just activate the “Do Not Track” option in your browser and WeBrowse will discard all traffic coming from your browser.
Chrome
Firefox
Internet Explorer

Safari
Contacts
- Giuseppe Scavo PhD candidate, Inria, Nokia Bell Labs, France
- Zied Ben Houidi Researcher, Nokia Bell Labs, France
- Prof. Renata Teixeira, Inria, France
To contact us, send an email to Renata.



