 Over the years, electrical stimulation (ES) has been used to activate paralyzed muscles to support rehabilitation. ES applied to fully or partially paralyzed muscles artificially induces muscle contraction substituting or completing the normal volitional control. When applied to function restoration (motor or sensory), the technique is usually called Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES).
Over the years, electrical stimulation (ES) has been used to activate paralyzed muscles to support rehabilitation. ES applied to fully or partially paralyzed muscles artificially induces muscle contraction substituting or completing the normal volitional control. When applied to function restoration (motor or sensory), the technique is usually called Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES).
The use of FES in individuals with Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) can result in significant benefits to users, such as reduced muscular atrophy, more efficient voluntary muscle engagement in different daily activities, increased bone density, improved cardiovascular function, decreased muscle spasticity, as well as other physical and psychological benefits.
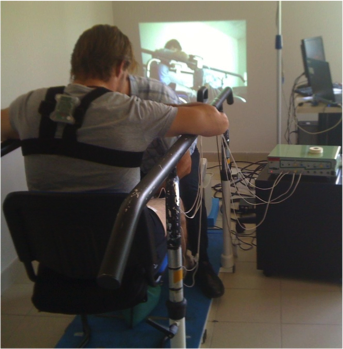 Transfer assistance is an example of the possible applications of FES. Functional transfers are essential to ensure basic activities of daily living of SCI subjects. The ability to transfer promotes social participation by which the quality of life is improved. Subjects who had their lower limbs paralyzed following SCI perform Sitting Pivot Transfer (SPT) 15 to 20 times a day using their preserved upper limbs. Despite the daily life benefits offered by using upper limbs during SPT, repetitive overload on shoulder joint surfaces should be avoided to prevent pain and degeneration. Several studies suggested different types of assistive devices to activate paralyzed muscles during transfers.
Transfer assistance is an example of the possible applications of FES. Functional transfers are essential to ensure basic activities of daily living of SCI subjects. The ability to transfer promotes social participation by which the quality of life is improved. Subjects who had their lower limbs paralyzed following SCI perform Sitting Pivot Transfer (SPT) 15 to 20 times a day using their preserved upper limbs. Despite the daily life benefits offered by using upper limbs during SPT, repetitive overload on shoulder joint surfaces should be avoided to prevent pain and degeneration. Several studies suggested different types of assistive devices to activate paralyzed muscles during transfers.
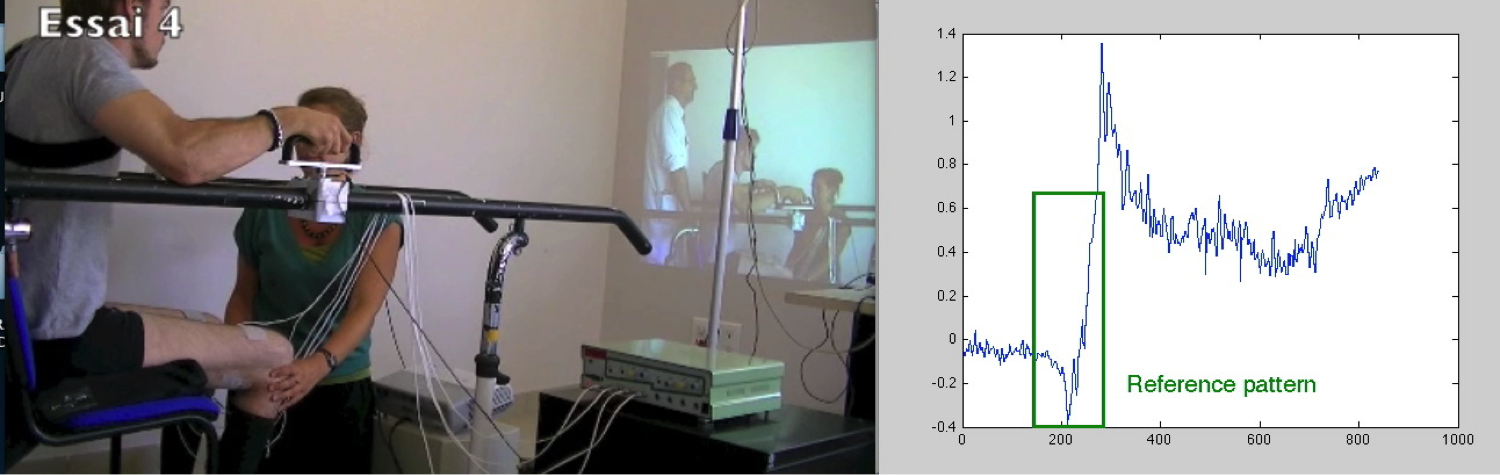
DEMAR team has proposed an original approach of FES assisted Sit to stand and standing. Preliminary results show tha t, in order to obtain reduced arm support participation, coordination between trunk motion and electrically stimulated lower limbs plays an important role. Most notably, lower limb stimulation should take place before the patient’s maximum trunk extension, right before the lift-off phase.
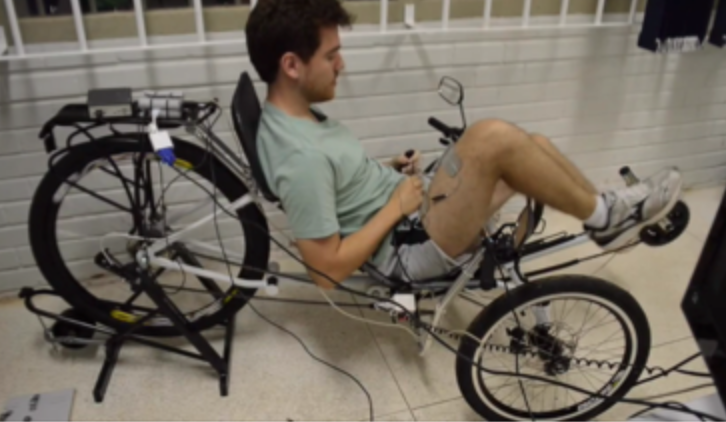 Another FES application for SCI individuals is FES cycling. Despite the permanent neurological deficits leading to muscle paralysis in lower limbs, SCI individuals have a life expectancy close from normal population. However, post-injury lifefollows with associated complications, mostly attributable to sedentarity, which could be avoided by regular exercise, noticeably is assisted by FES cycling. Ergocycles equip rehabilitation centers for many years now but outdoor cycling remains marginal (HASOMED©, BERKELBIKE©). The main limitation being muscle fatigue. Research published on this topic is usually centered on physiological benefits of cycling training.
Another FES application for SCI individuals is FES cycling. Despite the permanent neurological deficits leading to muscle paralysis in lower limbs, SCI individuals have a life expectancy close from normal population. However, post-injury lifefollows with associated complications, mostly attributable to sedentarity, which could be avoided by regular exercise, noticeably is assisted by FES cycling. Ergocycles equip rehabilitation centers for many years now but outdoor cycling remains marginal (HASOMED©, BERKELBIKE©). The main limitation being muscle fatigue. Research published on this topic is usually centered on physiological benefits of cycling training.
We aim at proposing approaches and solutions that can have an effect on patients quality of life , thus our choices intend to be realistic form a practical point of view.

